OverTheWire Krypton Level 6 → 7 tutorial!!
Login
ssh krypton6@krypton.labs.overthewire.org -p 2231
# password: RANDOM
Why? Each level uses a different UNIX account. The password is passed forward from Level 5 → 6.
Task
This level introduces a stream cipher.
You are given an encrypt6 binary that uses a hidden keyfile.dat plus a weak “random” generator.
Your target is /krypton/krypton6/krypton7, which is encrypted with the same mechanism.
Hints in the level suggest:
- The random generator is periodic (8‑bit LFSR).
- You can run chosen‑plaintext attacks (
encrypt6lets you encrypt any file). - With the pattern, you can replicate the keystream and decrypt the password.
Solution
1. Setup workspace
cd /tmp
mkdir -p kr6 && cd kr6
ln -s /krypton/krypton6/keyfile.dat .
Why? Working in /tmp is clean and safe; the symlink lets encrypt6 read the original keyfile.
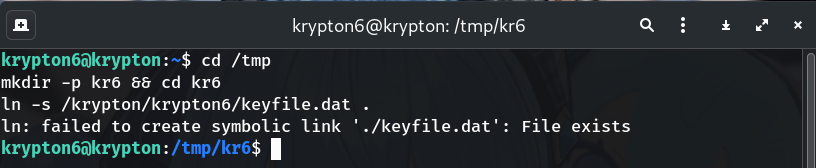
2. Create a file of 'A's and encrypt (to leak the keystream)
python3 - <<'PY'
open('a.txt','w').write('A'*50)
PY
/krypton/krypton6/encrypt6 a.txt outA.txt
cat outA.txt
You should see a repeating keystream block (~30 chars):
EICTDGYIYZKTHNSIRFXYCPFUEOCKRNEICTDGYIYZKTHNSIRFXY...
Why? With plaintext all 'A', ciphertext directly equals the keystream for each position.
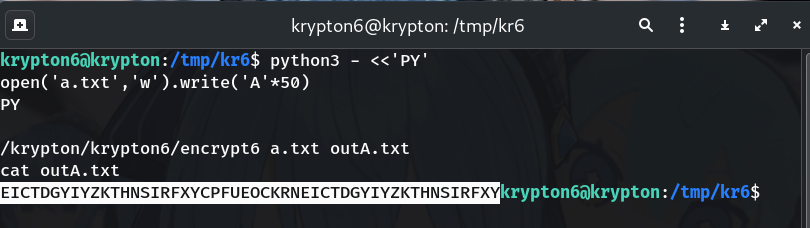
3. (Optional) Confirm with 'B's
python3 - <<'PY'
open('b.txt','w').write('B'*50)
PY
/krypton/krypton6/encrypt6 b.txt outB.txt
cat outB.txt
The pattern is identical but shifted by +1 (classic Caesar-on-top behavior).
4. Decrypt the target file
Extract the keystream period and apply it to krypton7.
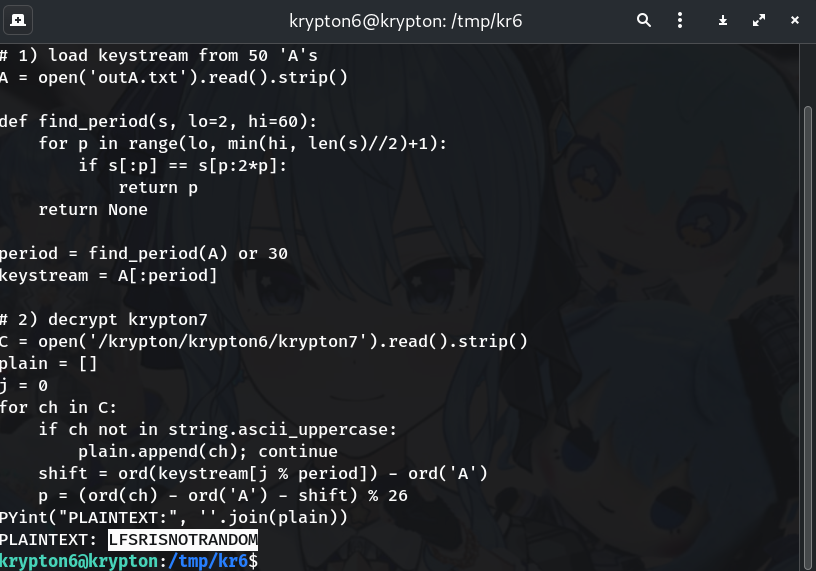
python3 - <<'PY'
import string
# 1) load keystream from 50 'A's
A = open('outA.txt').read().strip()
def find_period(s, lo=2, hi=60):
for p in range(lo, min(hi, len(s)//2)+1):
if s[:p] == s[p:2*p]:
return p
return None
period = find_period(A) or 30
keystream = A[:period]
# 2) decrypt krypton7
C = open('/krypton/krypton6/krypton7').read().strip()
plain = []
j = 0
for ch in C:
if ch not in string.ascii_uppercase:
plain.append(ch); continue
shift = ord(keystream[j % period]) - ord('A')
p = (ord(ch) - ord('A') - shift) % 26
plain.append(chr(p + ord('A')))
j += 1
print("PLAINTEXT:", ''.join(plain))
PY
Result:
PLAINTEXT: LFSRISNOTRANDOM
Password
LFSRISNOTRANDOM
Troubleshooting
- “Command ‘import’ not found” → You pasted Python into bash. Run it via a here‑doc:
python3 - <<'PY' ... PY. - No repeating pattern in
outA.txt→ Ensure you encrypted 50× ‘A’ from the same directory that has thekeyfile.datsymlink. - Mixed case / spaces → The mapping assumes uppercase A–Z only. Strip spaces/newlines when comparing.
- Wrong plaintext → Recreate
outA.txtand rerun the decrypt step; verifyperiodis around 30. - “File exists” when linking → Harmless. The symlink is already there; proceed.
- Ciphertext longer than your keystream → The keystream repeats; the code already indexes with modulo
period.
Congrats 🎉 You just broke the weak stream cipher using chosen‑plaintext analysis and keystream repetition. Krypton solved up to Level 7 (final)!


